
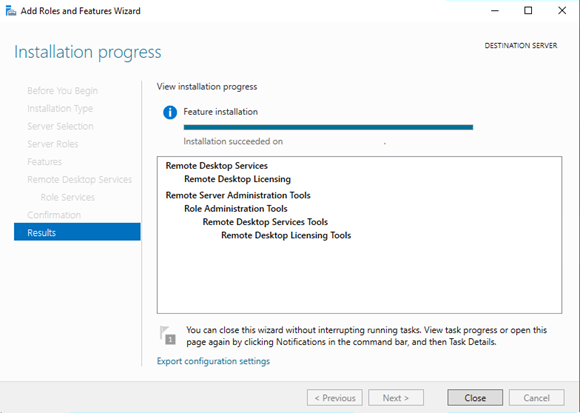
However, large deployments require them to be installed on separate servers.Įarlier editions of the Windows Server OS came with Terminal Services licenses. Small networks can have both the licensing service and RDSH on the same server. Regardless of the size of your RDS deployment, there should be at least one RD licensing server in the network. These CALs are installed and managed on the RD license server by the RD licensing service. After obtaining the appropriate CAL from the licensing server, it is delivered to the client device, and the connection is activated. Then on behalf of the client device that is connecting to the RDSH, the server contacts the Remote Desktop License Server and requests a CAL. When the client devices connect to the server using an RDP protocol, the server checks to see if the client requires an RDS CAL.
How Does Remote Desktop Server Licensing Work?Ī Remote Desktop Service Client Access License (RDS CAL) is needed for all client devices to access server resources.

When setting up RDS environments, you need to check licenses and policies. It allows businesses to host resources and securely publish them to remote devices centrally. RDS was formerly known as Terminal Services. Owing to its popularity and its inclusion in the Windows Server operating system, RDS is often the first choice for many businesses when it comes to setting up hosted applications and desktop networks. With the technology world turning toward the cloud, containerization and virtualization, Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS) have become a key component of business networks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
